Changes
Page history
Update associations
authored
Jun 04, 2024
by
Lukas Damerau
Hide whitespace changes
Inline
Side-by-side
uml/associations.md
View page @
043b32a2
**Sources:**
http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.5 (Starting at PDF page 239)
# Associations
An Association classifies a set of tuples representing links between typed instances, e.g., two instances of classes at runtime.
### Example

# Aggregation and Composition
Aggregation and Composition are subsets of associations, i.e., they are specific cases of association.
In both aggregation and composition object of one class "owns" object of another class. But there is a small difference.
## Aggregation
Aggregation implies a relationship where the child can exist independently of the parent.
### Example

Lecture (parent) and Student (child). Delete the Lecture and the Students still exist.
## Composition
Composition implies a relationship where the child cannot exist independent of the parent.
### Example

Person (parent) and Head, Leg, and Heart (children). The children don't exist separate to a Person.
**Sources:**
http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.5 (Starting at PDF page 239)
# Associations
An Association classifies a set of tuples representing links between typed instances, e.g., two instances of classes at runtime.
### Example

# Aggregation and Composition
Aggregation and Composition are subsets of associations, i.e., they are specific cases of association.
In both aggregation and composition object of one class "owns" object of another class. But there is a small difference.
## Aggregation
Aggregation implies a relationship where the child can exist independently of the parent.
### Example
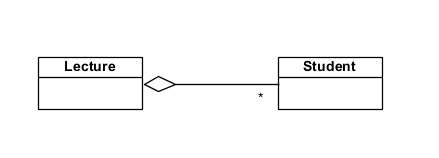
Lecture (parent) and Student (child). Delete the Lecture and the Students still exist.
## Composition
Composition implies a relationship where the child cannot exist independent of the parent.
### Example

Person (parent) and Head, Leg, and Heart (children). The children don't exist separate to a Person.